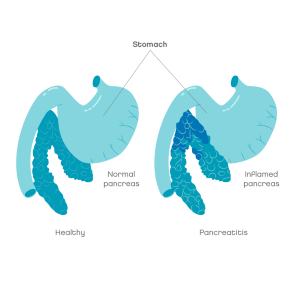
Pancreatitis is a serious and painful illness caused by inflammation of the pancreas. Around 1 in 100 dogs in the UK get pancreatitis. Dogs of any age, breed or sex are affected, but pancreatitis is most common in dogs over 7 years old and in certain breeds.
The pancreas is a gland in your dog’s tummy. It produces powerful chemicals, called enzymes, which break down food in the intestines. Sometimes the gland becomes swollen and painful. Common symptoms of pancreatitis include vomiting, nausea, and tummy pain. Dogs with pancreatitis need to see a vet. Severe pancreatitis needs intensive care in a vet hospital. Around 40% of dogs diagnosed with severe pancreatitis won’t survive the illness.
Overview
What is pancreatitis in dogs?
Pancreatitis is the inflammation of the pancreas.
- Pancreatitis may be sudden (acute), or come on gradually and last longer (chronic).
- The cause of pancreatitis is usually unknown. Vets call this ‘idiopathic’.
- Some breeds of dogs are more likely to get pancreatitis than others.
- Eating too much fatty (human) food can trigger pancreatitis
- Most dogs recover well from mild pancreatitis.
- Acute pancreatitis is a life-threatening illness
How does pancreatitis happen?
- Powerful digestive enzymes inside the pancreas activate too soon
- The enzymes attack the pancreas
- The pancreas becomes swollen and angry
- It stops working properly
Dogs who have had one bout of pancreatitis are more likely to suffer another one sometime in the future
There are two parts to the pancreas. These two parts have separate functions:
- The exocrine pancreas produces enzymes to digest food in the intestines.
- The endocrine pancreas produces hormones, mainly insulin. Insulin controls sugar levels in the blood.
Pancreatitis usually affects only the exocrine pancreas. But severe or recurrent pancreatitis may damage the endocrine part as well.
When the pancreas gets badly damaged, your dog may become unable to digest food (EPI). In rare cases, it can also lead to sugar diabetes (diabetes mellitus)
Symptoms
Symptoms of pancreatitis in dogs
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis
- Vomiting and dehydration
- Eating less or refusing food
- Lethargy (low energy)
- Diarrhoea
- A painful tummy – arched back, restless, lying with front end lower than back (‘praying position’)
- Drooling saliva
Call a vet if your dog has been vomiting for more than 24 hours or has abdominal pain.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis
Symptoms are similar, but come on more gradually
- Bouts of sickness that come and go
- Occasionally going off food
- Weight loss
- Lethargy
- A painful tummy
- A gurgly, bubbly tummy (also called borborygmi)
Call a vet if your dog has been vomiting for more than 24 hours or has abdominal pain
Risk
Dogs at higher risk of developing pancreatitis
Dogs with other health problems
- Obesity
- An underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism)
- Sugar diabetes (diabetes mellitus)
- Cushing’s disease (hyperadrenocorticism)
- Immune illnesses
- Certain infectious diseases (such as Leishmaniasis and Babesiosis)
Certain breeds
- Miniature Schnauzers
- Terrier breeds,
- Cocker spaniels,
- Poodles
Dogs with an inherited condition that causes high levels of fat in their blood
- Miniature Schnauzers
- Shetland Sheepdogs
Dogs receiving certain medications used to treat epilepsy (such as potassium bromide and phenobarbitone).
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of pancreatitis
There’s not a specific test for pancreatitis.
Vets diagnose pancreatitis based on
- Symptoms your dog is showing
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Ultrasound scan of the tummy to look at the structure and size of the pancreas
Vet treatment
Vet treatment for pancreatitis in dogs
There’s not a cure or specific treatment for pancreatitis.
Vets treat the symptoms of pancreatitis to give the inflamed pancreas a chance to recover.
- Medicine to treat vomiting and nausea
- Lots of fluids to prevent or treat dehydration
- Pain relief
- Antacid medicine
- A special low-fat prescription diet
Mild pancreatitis
If your dog is able to keep water down, they can be treated at home with prescription medicine – usually tablets or liquid, including:
- Anti-sickness medicine
- Pain relief
- Antacids
- Special prescription food
Severe pancreatitis
If your dog has severe pancreatitis and is dehydrated, they will need intensive treatment. This means staying in hospital for:
- Life-saving fluids via a drip directly into their leg
- Anti-sickness injections
- Strong pain-killing injections
- Feeding through a stomach tube: your dog needs nutrition to recover from pancreatitis, but may not want to eat. If your dog is very unwell, the vet may have to give this food via a tube directly into their stomach
Home treatment
Home remedies for pancreatitis in dogs
How to look after a dog with pancreatitis at home
Most dogs with mild pancreatitis will recover well at home with the right treatment and careful nursing:
- Give your dog medicine prescribed by your vet at the correct dose and time
- Encourage them to drink small frequent drinks or give them ice cubes
- Add water to food, especially warm water from cooking chicken breast
- Syringe small amounts of water directly into your dog’s mouth
- Use oral rehydration products (Oralade, Lectade)
- Offer small, frequent meals of light food, such as chicken or white fish and rice
- Keep your dog warm and quiet.
- Rest your dog, only taking them into the garden to toilet or a short distance on the lead
As your dog recovers from pancreatitis, feeding a low-fat diet will reduce the workload on the pancreas and help reduce the risk of pancreatitis recurring.
Living with a dog with pancreatitis
Even after they get better, dogs sometimes suffer from recurrent bouts of pancreatitis later on.
Feeding the right diet and recognising the early signs of pancreatitis will help to keep your dog as healthy as possible for the longest time.
- Feed a balanced, low-fat diet
- Only give your dog low-fat treats
- Make sure you have healthy options handy if visitors or friends want to give your dog a treat. Carrots are a great alternative.
- Learn to recognise the symptoms of pancreatitis in your dog
- Call a vet as soon as possible if you recognise the familiar signs of a relapse
Prevention
Tips on how to prevent pancreatitis in dogs
We don’t know for certain what triggers pancreatitis, but you can reduce your dog’s risk by:
- Ensuring your dog eats a healthy diet
- Keeping your dog fit and slim
- Avoiding human foods as treats, especially fatty, sugary and processed foods
- Treating and monitoring other illnesses under veterinary advice
- Being particularly careful if your dog is in a higher risk group or breed
When to worry
When to worry about your dog with pancreatitis
Most dogs with mild pancreatitis will start to improve within a day or two of starting the right treatment. Sometimes recovery is less straightforward and your dog needs more help to get better.
Contact your nearest vet practice now if your dog:
- Has collapsed after persistent vomiting
- Is hunched with abdominal pain and unable to settle
- Has developed rapid or shallow breathing
- Looks pale and hard to rouse
- Has deteriorated despite treatment
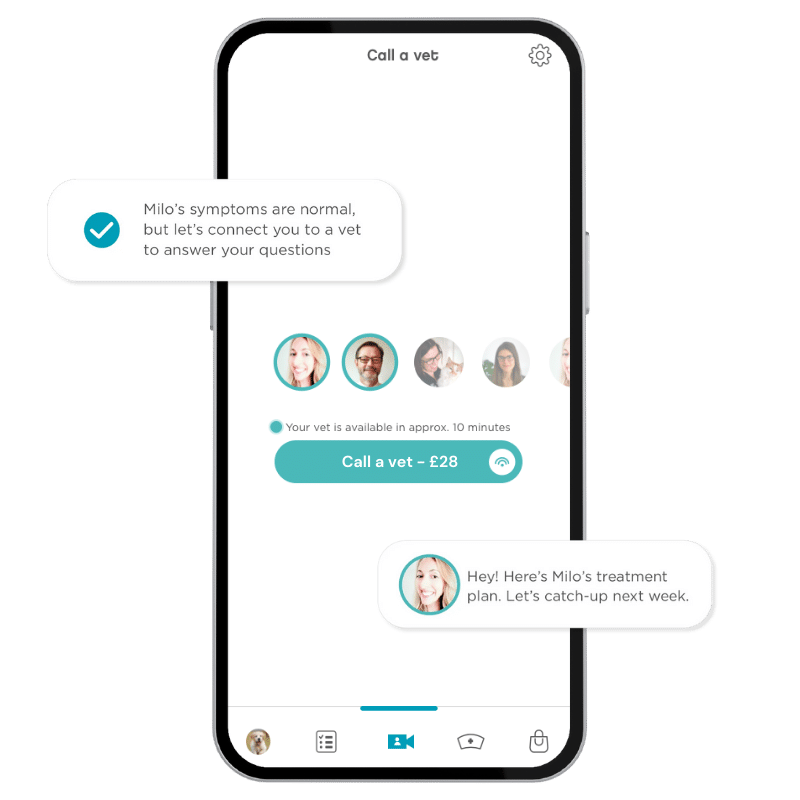
Joii can help with:
- Recognising the signs of pancreatitis
- Managing chronic pancreatitis
- Ensuring your dog doesn’t get dehydrated
- Tempting your dog to eat
- Choosing low-fat diets
- Changing harmful eating habits